Connecting VB 6 to Oracle Database
We can connect to vb6 with oracle by two methods :
1.Using ADO data control.
2.Using ADO object.
1.Using ADO data control to connect to oracle:
First you have to know your hostname for oracle server you are using.This can be found in the TNSNAMES file which comes installed along with the oracle.You just need to locate the file and find the host name.Most commonly the host name is like "localhost" or anything.Now with knowing your host name connecting to oracle is easy.
First, let's add the ADO Data Control to the Visual Basic Toolbox by selecting Project-Components from the Visual Basic Menu Bar, then selecting
Microsoft ADO Data Control 6.00 (be sure it has OLEDB at theend of the name) and clicking the OK Button.
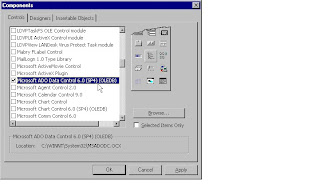 For this demonstration, we'll be populating a Data Grid with the data from the Employees table in an Oracle table I've built. We need to add the Data Grid to the Visual Basic Toolbox first, and we do that just the way we added the ADO Data Control by selecting Project-Components from the Visual Basic Menu Bar. An important point here---you must use the OLEDB version of the DataGrid in conjunction with the ADO Data Control---as you can see in the screen shot below, this DataGrid has the word OLEDB after it in the selection list. DON'T select the Data Bound Grid Control 5.0 --- that grid can only be used with the DAO Data Control.
For this demonstration, we'll be populating a Data Grid with the data from the Employees table in an Oracle table I've built. We need to add the Data Grid to the Visual Basic Toolbox first, and we do that just the way we added the ADO Data Control by selecting Project-Components from the Visual Basic Menu Bar. An important point here---you must use the OLEDB version of the DataGrid in conjunction with the ADO Data Control---as you can see in the screen shot below, this DataGrid has the word OLEDB after it in the selection list. DON'T select the Data Bound Grid Control 5.0 --- that grid can only be used with the DAO Data Control.
As you can see, both the ADO Data Control and the DataGrid Control have been added to the Visual Basic Toolbox.
With both controls in your Toolbox, now it's time to add them to your form.
Bring up the Properties window for your ADO Data Control and select the Connection Property--this is the key to achieving the connection. The three dots (ellipsis) indicates that a window will open for you when you click on it.
This is a Property Page for the Connection Property. Click on the Build button to start 'building' the Connection String.
And this window will appear, asking you to select the Provider for your database. For Oracle, you want to select the Microsoft OLE DB Provider for Oracle. Do so, then click on the Next button.
The Oracle Connection requires that you designate a Server name, a User Name, and a Password. The Server name is the name of your Host File as designated in the TNSNAMES file I mentioned earlier. In my instance, it is 'local host'. My User name is 'paul' and my password is (well, that's a secret). Notice how I have checked 'Allow saving password'---this eliminates a nasty popup dialog box prompting you for a password from appearing when you execute the program containing this connection.
Enter your own Host Name, User name and Password for your Oracle database.
Be sure to test the connection by clicking on the 'Test Connection' button.
If the information you supply is correct, you should see this dialog box appear.
If the information you supply is incorrect, you'll receive this sad message.
If that happens, check with your Oracle Database Administrator to verify the name of your Host File, your User Name and Password.
If your connection test proves successful, click on the OK button and you should notice that the Connection String Property of your Data Control has been filled in for you.
When we discuss using ADO Objects to achieve your connection, the Connection String value that you see here will be used in code.
Now that you've verified your Connection, you've done the work necessary to open your Oracle Database---now you need to tell Visual Basic the exact information you require. This could be a table name, or it could be a recordset built by a SQL Statement. Regardless, you need to provide some information to Visual Basic in the RecordSource property of the ADO Data Control. Select the RecordSource Property. Again, the three dots (ellipsis) indicates that a window will open up when you click on it.
The easiest type of connection to achieve is one where you specify a table name, and you start that process by selecting adCmdTable in the Command Type dropdown listbox. When you do so, a list of tables for your database will appear in the Table or Stored Procedure Name dropdown listbox. My Oracle database contains two tables, Employees and Vendors. I'll select Employees.
You could also choose to build your connection using a SQL statement instead of a single table name.SQL statements allow you to build a recordset with information from more than one table.To specify a SQL statement instead of a table name ,specify adCmdtText as the Command Type and enter your SQL Statement into the Command Text Textbox.
Either way, click on the OK button, and you should see that the RecordSource property of your Data Control now has a value.
The last step is to bind the ADO Data Control to another control capable of displaying the data from our Oracle table. For demonstration purposes, nothing could be easier than the DataGrid. Bring up its Property window, and select the ADO Data Control for its DataSource property.
Now run the program, and you see that the DataGrid is now populated with the data present in the Employees table of your Oracle database.
2.Using ADO object.
1.Using ADO data control to connect to oracle:
First you have to know your hostname for oracle server you are using.This can be found in the TNSNAMES file which comes installed along with the oracle.You just need to locate the file and find the host name.Most commonly the host name is like "localhost" or anything.Now with knowing your host name connecting to oracle is easy.
First, let's add the ADO Data Control to the Visual Basic Toolbox by selecting Project-Components from the Visual Basic Menu Bar, then selecting
Microsoft ADO Data Control 6.00 (be sure it has OLEDB at theend of the name) and clicking the OK Button.
 For this demonstration, we'll be populating a Data Grid with the data from the Employees table in an Oracle table I've built. We need to add the Data Grid to the Visual Basic Toolbox first, and we do that just the way we added the ADO Data Control by selecting Project-Components from the Visual Basic Menu Bar. An important point here---you must use the OLEDB version of the DataGrid in conjunction with the ADO Data Control---as you can see in the screen shot below, this DataGrid has the word OLEDB after it in the selection list. DON'T select the Data Bound Grid Control 5.0 --- that grid can only be used with the DAO Data Control.
For this demonstration, we'll be populating a Data Grid with the data from the Employees table in an Oracle table I've built. We need to add the Data Grid to the Visual Basic Toolbox first, and we do that just the way we added the ADO Data Control by selecting Project-Components from the Visual Basic Menu Bar. An important point here---you must use the OLEDB version of the DataGrid in conjunction with the ADO Data Control---as you can see in the screen shot below, this DataGrid has the word OLEDB after it in the selection list. DON'T select the Data Bound Grid Control 5.0 --- that grid can only be used with the DAO Data Control.As you can see, both the ADO Data Control and the DataGrid Control have been added to the Visual Basic Toolbox.
With both controls in your Toolbox, now it's time to add them to your form.
Bring up the Properties window for your ADO Data Control and select the Connection Property--this is the key to achieving the connection. The three dots (ellipsis) indicates that a window will open for you when you click on it.
This is a Property Page for the Connection Property. Click on the Build button to start 'building' the Connection String.
And this window will appear, asking you to select the Provider for your database. For Oracle, you want to select the Microsoft OLE DB Provider for Oracle. Do so, then click on the Next button.
The Oracle Connection requires that you designate a Server name, a User Name, and a Password. The Server name is the name of your Host File as designated in the TNSNAMES file I mentioned earlier. In my instance, it is 'local host'. My User name is 'paul' and my password is (well, that's a secret). Notice how I have checked 'Allow saving password'---this eliminates a nasty popup dialog box prompting you for a password from appearing when you execute the program containing this connection.
Enter your own Host Name, User name and Password for your Oracle database.
Be sure to test the connection by clicking on the 'Test Connection' button.
If the information you supply is correct, you should see this dialog box appear.
If the information you supply is incorrect, you'll receive this sad message.
If that happens, check with your Oracle Database Administrator to verify the name of your Host File, your User Name and Password.
If your connection test proves successful, click on the OK button and you should notice that the Connection String Property of your Data Control has been filled in for you.
When we discuss using ADO Objects to achieve your connection, the Connection String value that you see here will be used in code.
Now that you've verified your Connection, you've done the work necessary to open your Oracle Database---now you need to tell Visual Basic the exact information you require. This could be a table name, or it could be a recordset built by a SQL Statement. Regardless, you need to provide some information to Visual Basic in the RecordSource property of the ADO Data Control. Select the RecordSource Property. Again, the three dots (ellipsis) indicates that a window will open up when you click on it.
The easiest type of connection to achieve is one where you specify a table name, and you start that process by selecting adCmdTable in the Command Type dropdown listbox. When you do so, a list of tables for your database will appear in the Table or Stored Procedure Name dropdown listbox. My Oracle database contains two tables, Employees and Vendors. I'll select Employees.
You could also choose to build your connection using a SQL statement instead of a single table name.SQL statements allow you to build a recordset with information from more than one table.To specify a SQL statement instead of a table name ,specify adCmdtText as the Command Type and enter your SQL Statement into the Command Text Textbox.
Either way, click on the OK button, and you should see that the RecordSource property of your Data Control now has a value.
The last step is to bind the ADO Data Control to another control capable of displaying the data from our Oracle table. For demonstration purposes, nothing could be easier than the DataGrid. Bring up its Property window, and select the ADO Data Control for its DataSource property.
Now run the program, and you see that the DataGrid is now populated with the data present in the Employees table of your Oracle database.
No comments:
Post a Comment